Rehabilitation Program
● Post Operation Condition
● Stroke
● Spinal Cord Injury
● Brain Injury
● Bedridden Condition
Post Operation
Condition

Some of the things we do for post-operative conditions such as Fracture, Total Hip Replacement, and Total Knee Replacement are as below:
- Conducting a thorough assessment of the patient’s condition to determine the appropriate rehabilitation program.
- Designing and implementing an individualized rehabilitation program that may include exercises to restore range of motion, muscle strength, and flexibility.
- Providing education to patients on proper wound care, positioning, and safe movement to prevent further injury or complications.
- Monitoring the patient’s progress and response to treatment, adjusting the rehabilitation program as necessary to ensure optimal recovery.
- Providing emotional support and guidance to patients as they navigate the challenges of rehabilitation and adjust to life after the fracture.
- Providing ongoing support and guidance to patients as they transition from rehabilitation to resuming their normal activities of daily living.
Stroke
Some of the things we do for a rehabilitation program for stroke patients are as below:
- Conducting a thorough assessment of the patient’s condition to
determine the appropriate rehabilitation program. - Designing and implementing an individualized rehabilitation program that may include exercises to restore movement, strength, and flexibility.
- Focusing on improving walking, balance, and coordination to help patients regain independence and reduce the risk of falls.
- Providing education to patients and their caregivers on proper positioning and techniques for activities of daily living, such as getting in and out of bed, dressing, and grooming.
- Providing education to patients and their caregivers on the importance of regular exercise, a healthy diet, and other lifestyle factors that can improve overall health and wellbeing.
- Providing emotional support and guidance to patients as they navigate the challenges rehabilitation and adjust to life after stroke.
- Collaborating with other healthcare professionals, such as neurologists, speech therapists, and occupational therapists, to ensure a comprehensive approach to patient care and optimize outcomes.
- Monitoring the patient’s progress and response to treatment, adjusting the rehabilitation program as necessary to ensure optimal recovery.
- Providing ongoing support and guidance to patients as they transition from rehabilitation to resuming their normal activities of daily living.

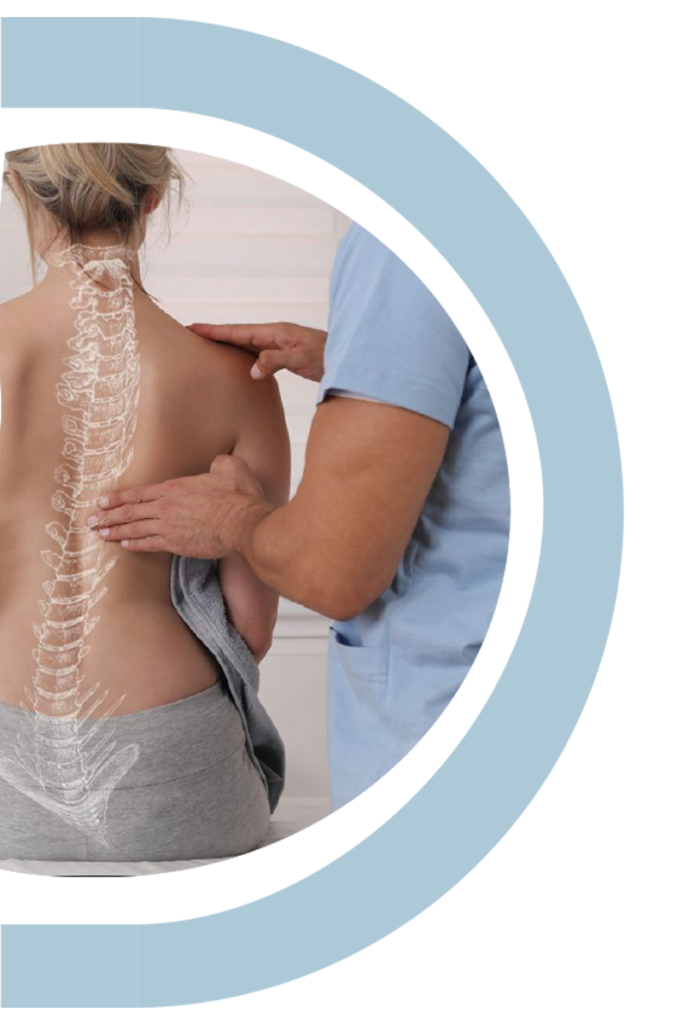
Spinal Cord Injury
- Conducting a thorough assessment of the patient’s condition to determine the appropriate rehabilitation program.
- Designing and implementing an individualized rehabilitation program that may include exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and coordination.
- Focusing on improving mobility and functional abilities, such as sitting, standing, and walking, depending on the level and severity of the injury.
- Providing education to patients and their caregivers on proper positioning and techniques for activities of daily living, such as transferring in and out of a wheelchair, bathing, and dressing.
- Providing education to patients and their caregivers on the importance of regular exercise, a healthy diet, and other lifestyle factors that can improve overall health and wellbeing.
- Providing emotional support and guidance to patients as they navigate the challenges of rehabilitation and adjust to life after SCI.
- Collaborating with other healthcare professionals, such as neurologists, occupational therapists, and speech therapists, to ensure a comprehensive approach to patient care and optimize outcomes.
- Monitoring the patient’s progress and response to treatment, adjusting the rehabilitation program as necessary to ensure optimal recovery.
- Providing ongoing support and guidance to patients as they transition from rehabilitation to resuming their normal activities of daily living.
- Recommending assistive devices, such as braces, crutches, or wheelchairs, to help patients move around safely and independently.
- Providing instruction on specialized equipment, such as electrical stimulation devices or standing frames, to help patients maintain or improve muscle function and range of motion.
Brain Injury
What We Do For Brain Injury Patients
- Conducting a thorough assessment of the patient’s condition to determine the appropriate rehabilitation program.
- Designing and implementing an individualized rehabilitation program that may include exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and coordination.
- Focusing on improving mobility and functional abilities, such as sitting, standing, and walking, depending on the level and severity of the injury.
- Providing education to patients and their caregivers on proper positioning and techniques for activities of daily living, such as transferring in and out of bed or a wheelchair, bathing, and dressing.
- Providing education to patients and their caregivers on the importance of regular exercise, a healthy diet, and other lifestyle factors that can improve overall health and wellbeing.
- Providing emotional support and guidance to patients as they navigate the challenges of rehabilitation and adjust to life after brain injury.
- Collaborating with other healthcare professionals, such as neurologists, occupational therapists, speech
Bed Ridden
What We Do For Bed Ridden Patients
- Conducting a thorough assessment of the patient’s condition to determine the appropriate rehabilitation program.
- Designing and implementing an individualized rehabilitation program that may include exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and mobility.
- Focusing on preventing complications such as pressure sores, muscle weakness, and joint stiffness.
- Providing education to patients and their caregivers on proper positioning and techniques for activities of daily living, such as turning in bed, transferring to a wheelchair, and hygiene care.
- Providing education to patients and their caregivers on the importance of regular exercise, a healthy diet, and other lifestyle factors that can improve overall health and wellbeing.
- Providing emotional support and guidance to patients as they navigate the challenges of being bedridden.
- Collaborating with other healthcare professionals, such as nurses and occupational therapists, to ensure a comprehensive approach to patient care and optimize outcomes.
- Monitoring the patient’s progress and response to treatment, adjusting the rehabilitation program as necessary to ensure optimal recovery.
- Recommending assistive devices, such as bed rails or specialized mattresses, to help patients maintain proper body alignment and prevent falls or injuries.
- Providing instruction on passive range of motion exercises to prevent joint contractures and improve circulation.
- Providing instruction on deep breathing exercises and chest physiotherapy to prevent respiratory complications.
